DP Flowmeters: Standing Up Under Pressure (Part 1 of 2)
By David Spitzer
A differential pressure (DP) flow measurement system consists of a DP primary flow element and a DP flow transmitter. When the flow of a fluid in a pipe passes a restriction in a piping system, pressure in the piping system is reduced. Most DP primary flow elements are designed, constructed and operated in a manner such that the flow rate is proportional to the square root of the pressure drop across the restriction. These primary flow elements include orifice plates, Venturi tubes, elbows, flow nozzles, low loss flow tubes, single-port and multiple-port Pitot tubes, segmental wedge, and V-Cone flowmeters.
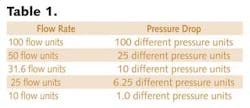
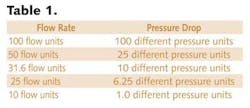
Some DP primary flow elements, such as critical flow elements and laminar flow elements, don't follow this (squared) relationship. Therefore, some sections of this article don't apply to these technologies. As mentioned above, the flow rate through a DP primary flow element is proportional to the square root of the pressure drop across the restriction. Table 1 illustrates this.
The relationship can limit ability of DP flowmeter technology to measure large flow ranges. In the table above, a "reasonable" flow measurement range of 10-100 flow units (10:1 flow turndown) would require a DP flow transmitter range of 1-100 differential pressure units (100:1 DP turndown). Therefore, the "reasonable" 10:1 flow turndown requires a 100:1 DP flow transmitter turndown.
Because many DP flow transmitters measured accurately with an approximate 10:1 DP turndown, DP flowmeter technology was often considered accurate from about 30-100 flow units. Improved performance of DP flow transmitters has increased the DP turndown, so somewhat larger flow turndowns may be possible.
The upstream and downstream pressures associated with a DP primary flow element are available at the taps of the element. Both of these taps are piped to ports on the DP flow transmitter that measures the pressure drop. The flow transmitter is a device that converts the differential pressure across its ports into an analog signal. When the DP flow transmitter has an integral square root function, its output signal can be linear with flow rate.
Some (multivariable) DP flow transmitters can make multiple measurements, such as differential pressure, pressure and/or temperature, from which the flow rate can be calculated. These transmitters are outside the scope of this report.
In general, wetted parts (such as diaphragms) in contact with the fluid provide movement or force that's related to the differential pressure across the transmitter pressure ports. DP flow transmitters have been designed using many technologies including capacitance, differential transformer, force balance, piezoelectric, potentiometer, strain gage and vibrating wire.
The quality of a DP flow transmitter signal can be described by its performance specifications. Therefore, given performance specifications, the (internal) sensing technology and details of (internal) operation aren't overly important concerns when considering the purchase of DP flow transmitters (although some sensing technologies may have superior reputations).
Due to the nature of the nonlinear relationship between flow and differential pressure, relatively small differential pressure changes can result in relatively large flow changes at low flow rates. To reduce the noise associated with the flow signal at these flows, some DP transmitters force their output signal to zero flow when the signal falls below a certain (preset) differential pressure. Some transmitters with integral square root extraction use a linear relationship between flow and differential pressure below a certain (preset) flow rate. Other algorithms may be available to stabilize the output signal at low flow rates.
The construction of DP flow transmitters is such that its wetted parts can be made from materials that can withstand corrosion. In typical installations, impulse tubes are installed such that no flow occurs at the transmitter, so abrasion and wear aren't usually important concerns. Abrasion and wear, however, can affect performance of a DP primary flow element by affecting its geometry. DP flow transmitters can measure the flow of many corrosive liquids, gases, and vapors. These flow elements with appropriate geometries and materials of construction can withstand abrasive fluids.
Differential pressure flow transmitters can be constructed of materials that don't contaminate the fluid. They aren't generally applied to sanitary service, though, because of limitations on the ability to clean them.